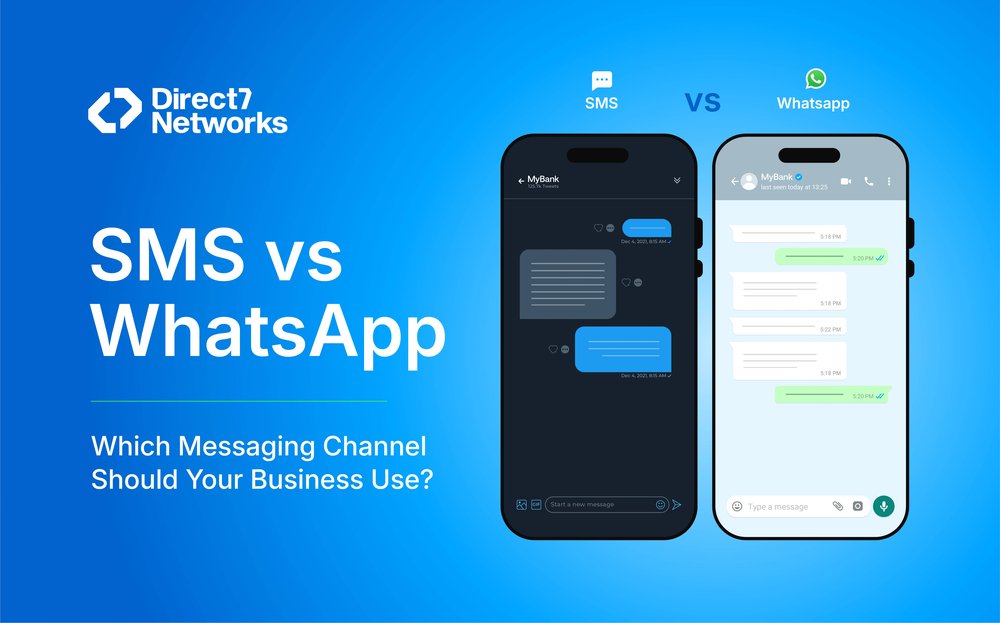
Both SMS and WhatsApp connect with people on the device they check the most daily their mobile phones. But the two channels differ in rules, message formats, costs, and compliance expectations. This guide breaks down when to use SMS, when to use WhatsApp, and when a hybrid approach makes sense.
1) The short answer
Choose SMS when…
- You need universal reach.
- Sending quick, one-time alerts like OTPs or delivery updates.
- Your contact lists include numbers without app adoption.
Works on virtually every mobile phone number worldwide.
Choose WhatsApp when…
- Your audience is already active on WhatsApp.
- You want rich, branded, two-way conversations that support:
- Media (images, PDFs, audio, video).
- Interactive elements (buttons, lists).
- Reliable read receipts.
- Especially effective for customer support and repeat engagement.
Use Both when…
- Your audience is mixed across markets.
- Strategy:
- Default to WhatsApp in regions with high adoption.
- Fall back to SMS for first-touch messages or failover delivery.
Takeaway: SMS = universal reliability. WhatsApp = rich engagement. A dual strategy = best of both worlds.
2. Reach and Audience Fit
SMS
- If a phone number can receive texts, you can reach it.
- No app install required → makes SMS the baseline for time-sensitive notifications and OTPs worldwide.
- Massive global user base with strong penetration in:
- India
- Brazil
- Most of Latin America
- The Middle East
- Large parts of Europe
- Adoption is lower in markets like the United States, so country-level segmentation is key.
- For audiences who already chat daily on WhatsApp, engagement is higher—conversations feel natural, threaded, and richer.
Takeaway
- Look at your top customer markets:
- High WhatsApp penetration? → Lean heavily into WhatsApp.
- Low adoption? → Keep SMS as primary and layer WhatsApp progressively.
Summary: SMS guarantees reach; WhatsApp enhances interaction. The right choice depends on where your customers are and how they prefer to communicate.
3. Message Types and Capabilities
SMS and WhatsApp differ significantly in content options, interactivity, and branding features.
SMS
- Content:
- Plain text by default.
- MMS can add images or media, but support and pricing vary by country.
- Length:
- One SMS segment = 160 GSM-7 characters.
- Using Unicode (e.g., emojis, non-Latin characters) reduces this to 70 characters.
- Longer texts are automatically split into multiple segments.
- Interactivity:
- Limited to:
- Links.
- Keyword replies (e.g., “STOP”, “HELP”).
- Limited to:
- Receipts:
- Delivery receipts depend on the carrier/device.
- Read receipts are not supported.
- Content:
- Supports rich messages including:
- Images, video, audio.
- File attachments (PDFs, docs).
- Location sharing.
- Product catalogs.
- List messages and interactive reply buttons.
- Supports rich messages including:
- Structure:
- Free-form replies allowed within a 24-hour customer-service window after a user messages you.
- If you message first (or outside the 24-hour window), you must use an approved template.
- Receipts:
- Strong transparency: sent, delivered, and read statuses.
- Users may disable read receipts, but delivery status remains reliable.
- Branding:
- Create a business profile with:
- Logo.
- Description.
- Create a business profile with:
- Some brands qualify for an official business account badge for credibility.
Takeaway
- Use WhatsApp when you need:
- Structured prompts.
- Product pickers or catalogs.
- Media-heavy or interactive customer journeys.
- Use SMS when you need:
- Short, universal alerts (OTPs, order updates).
- Guaranteed delivery to any handset, anywhere.
4. Consent and Compliance
Both SMS and WhatsApp are consent-first channels, but each comes with its own regulatory framework and operational rules.
SMS Compliance
- Opt-In Requirements
- Many regions require explicit opt-in before sending marketing texts.
- Examples:
- TCPA (U.S.) → Prior consent required.
- GDPR/ePrivacy (EU/UK) → Consent required for marketing.
- Opt-Out Handling
- Must honor STOP (unsubscribe) and HELP (assistance) keywords.
- Opt-outs must be processed immediately.
- Sender Identification
- Messages must clearly show who the sender is.
- Include help information or support options.
- India (DLT)
- Requires DLT registration of:
- Principal Entity (business).
- Headers (sender IDs).
- Content templates (checked for compliance).
- All commercial messaging is scrubbed against consent/DND lists.
- Requires DLT registration of:
WhatsApp Compliance
- Opt-In Requirements
- Users must give explicit consent to receive WhatsApp messages.
- Consent must:
- Clearly state the business name.
- Specify the types of messages (e.g., updates, offers).
- Template Rules
- Marketing outside the 24-hour window requires an approved message template.
- Within the 24-hour customer-service window (after a user messages you):
- Free-form replies are allowed.
- No template is needed.
- The 24-hour clock resets each time a user sends a message.
Takeaway
- Both channels demand opt-in → You cannot skip consent.
- WhatsApp adds extra layers → Template approval + session timing (24-hour rule).
- SMS adds regional layers → Varying rules on time-of-day restrictions, disclosures, DND lists, and mandatory registration (e.g., India’s DLT).
5. Pricing Models (What Changes Your Bill)
SMS and WhatsApp use different billing structures. SMS pricing is usually simple but fragmented across markets, while WhatsApp uses category-based pricing tied to message type and country.
SMS Pricing
- Per-Segment Billing
- SMS is usually billed per segment.
- Long messages are split into multiple segments and billed separately.
- International Variations
- Pricing depends on:
- Destination country.
- Carrier route used.
- Message type (transactional vs. promotional).
- Some countries apply surcharges, registration fees, or scrubbing charges (e.g., India’s DLT framework).
- Pricing depends on:
WhatsApp Pricing
- Category + Direction Billing
- Business-initiated messages → Usually require approved templates.
- Pricing varies by category:
- Marketing.
- Utility (e.g., order updates).
- Authentication.
- Cost also depends on the user’s country code.
- Free Service Window
- User-initiated messages within the 24-hour service window:
- Business replies are free of charge.
- This makes WhatsApp cost-efficient for customer support at scale.
- User-initiated messages within the 24-hour service window:
- Evolving Model
- WhatsApp pricing has changed multiple times in recent years.
- Watch for:
- Shifts from per-message to per-conversation billing.
- Updated category definitions.
Takeaway
- SMS → Costs are easy to predict at the segment level, but international fees can add complexity.
- WhatsApp → Often more cost-efficient for service and support (thanks to free reply windows). However, outbound marketing via templates is metered and varies by category and geography.
- Best Practice → Maintain a live cost model per market to forecast spend accurately.
6. Deliverability, Analytics, and Reliability
Both SMS and WhatsApp can reach your audience—but they differ in how delivery is confirmed, how analytics work, and how reliable the channel is under different conditions.
SMS
- Delivery
- Depends on carrier networks.
- Providers may supply delivery receipts (where supported), but these stop at the network/device level.
- Read receipts are not available.
- Sender Types
- Deliverability can vary depending on whether you use:
- Short codes.
- Long numbers.
- Alphanumeric IDs.
- Proper registration and compliance improve success rates.
- Deliverability can vary depending on whether you use:
- India (DLT)
- DLT scrubbing automatically blocks messages that don’t follow approved templates or headers.
- This ensures compliance but adds extra setup requirements.
- Delivery & Read Receipts
- Built-in sent, delivered, and read statuses.
- Users may disable read receipts, but delivery telemetry remains strong.
- Media Reliability
- Images, video, and file attachments are more resilient than MMS equivalents.
- Message Quality
- Template approval depends on quality and compliance.
- User feedback (blocks, reports) can affect your sending throughput over time.
Takeaway
- WhatsApp → Best for transparent analytics and guaranteed read status. Ideal when engagement and telemetry matter.
- SMS → Best for ubiquitous reach, including:
- Basic phones.
- Markets with low data or no app penetration.
- Bottom Line → Use WhatsApp when you want clarity; use SMS when you need coverage.
7. Security and Privacy
Messaging security differs sharply between SMS and WhatsApp.
SMS
- Encryption: Not end-to-end encrypted.
- Risks: Messages may be intercepted at carrier or device level.
- Best Practices:
- Avoid sending sensitive personal data or confidential information in plain SMS.
- For OTPs:
- Use short expiries.
- Enforce rate limits.
- Add application-side controls to minimize exposure.
- Encryption: Provides end-to-end encryption for user messages.
- Anti-Spam Safeguards: Uses templates and platform policies to reduce spam.
- Compliance:
- Requires explicit consent.
- Must honor opt-outs and comply with local data laws.
Takeaway
- WhatsApp → Stronger security model for sensitive topics.
- SMS → Still widely used for OTPs, but must be secured with strict app-side protections.
- Note: WhatsApp now supports dedicated authentication templates, making it a viable OTP option in many markets.
8. Onboarding Speed and Operational Overhead
Operational setup differs greatly between SMS and WhatsApp.
SMS
- Speed: Quick to launch in many markets.
- Requirements (varies by region):
- Sender ID registration.
- Pre-approved content templates.
- Brand/campaign registration in regulated markets.
- Impact: In some regions (e.g., India, Singapore), lead times are longer due to compliance checks.
- Setup Steps:
- Business verification (via Meta).
- Phone number setup tied to your account.
- Template approval for outbound messages.
- Consent: Must plan processes to collect and store explicit opt-ins.
- Operational Advantage: Once set up, the 24-hour customer-service window allows free-form replies for support without template costs.
Takeaway
- SMS → Faster for first sends, good for urgent launches.
- WhatsApp → More upfront work, but rewards with richer experiences, brand presence, and lower long-term support costs.
9. When SMS Wins
SMS remains indispensable in scenarios where universal reach and simplicity matter most.
- One-Time Passwords (OTPs) & Critical Alerts → Works on any handset, even without data or apps.
- Transactional Notifications → Reliable for large, mixed audiences across many countries.
- First-Touch Reach → Useful when you don’t yet have WhatsApp opt-ins.
- Fallback Channel → Acts as a backup when:
- A WhatsApp message fails delivery, or
- The user isn’t on WhatsApp.
10. When WhatsApp Wins
WhatsApp excels where interaction and engagement matter.
- Customer Support & Two-Way Service
- Threaded chats, media sharing, and quick replies reduce friction.
- The 24-hour free reply window lowers cost for support-heavy use cases.
- Guided Flows
- Structured order updates, rebooking flows, document exchange, product lists, and buttons.
- Nurture & Re-Engagement
- Best for repeat engagement with audiences who have opted in and use WhatsApp heavily.
- Authentication
- Increasingly used for OTPs in markets where users expect codes via WhatsApp.
Summary: WhatsApp wins for rich interactions, guided journeys, and cost-efficient service.
11. Using Both Together (A Practical Playbook)
The most effective strategy often blends SMS + WhatsApp, using each where it performs best.
Step 1. Map Your Markets
- Segment by country and device patterns.
- Flag markets with high WhatsApp adoption (India, Brazil, LATAM, much of the EU).
Step 2. Define Primary + Fallback
- Primary WhatsApp, fallback SMS → India, Brazil, LATAM, parts of Europe.
- Primary SMS, test WhatsApp growth → U.S. and other lower-adoption markets.
Step 3. Set Consent Collection
- SMS → Add clear consent + opt-out language everywhere numbers are captured.
- WhatsApp → Capture explicit opt-in, including:
- Business name.
- Message types.
- Timestamp and source of consent.
Step 4. Build Template Strategy (WhatsApp)
- Create clear, neutral templates for:
- Utility.
- Authentication.
- Marketing.
Keep copies short, personalized, and non-spammy to protect quality ratings.
Step 5. Design Routing Logic
- Try WhatsApp first if the user is opted-in.
- If undelivered or session expired:
- Switch to SMS fallback, or
- Trigger a WhatsApp template if rules allow.
Step 6. Track KPIs by Channel
- SMS → Delivery rate, segment usage, opt-outs, route latency.
- WhatsApp → Delivery + read rates, session vs. template ratio, CSAT (customer satisfaction), opt-in growth.
Step 7. Compliance Guardrails
- Enforce quiet hours/silence windows by region.
- Process STOP/UNSUBSCRIBE on SMS instantly
- Provide simple opt-out flows on WhatsApp
- Keep consent records ready for audits.
Step 8. Run an Experiment Calendar
- SMS Tests → Message length, link placement.
- WhatsApp Tests → Buttons/lists vs. plain text.
- Cross-Channel → Compare cost per resolved support ticket across SMS vs. WhatsApp.
Summary: A combined playbook = WhatsApp where possible, SMS where necessary. Done right, the two channels complement each other—balancing reach, richness, cost, and compliance.
12. Example Use-Case Blueprints
Below are practical channel blueprints showing how SMS and WhatsApp can complement each other in real-world scenarios.
Order & Delivery Updates
- WhatsApp (Primary)
- Flow: Order confirmed → interactive buttons (“Track” / “Change Address”) → share live location or updated delivery window.
- SMS (Fallback)
- Short text with a tracking URL.
- Address change routed to a web form or agent.
Account Security
- WhatsApp (Primary, in high-adoption markets)
- Use Authentication Templates with one-tap OTP autofill (where supported).
- SMS (Fallback)
- Send a short-lived numeric OTP.
- Apply rate limiting and lockouts after failed attempts.
Appointment Reminders
- WhatsApp (Primary)
- Reminder message + quick reply buttons: “Confirm / Reschedule.”
- Option to present a list of available slots for rescheduling.
- SMS (Fallback)
- Short reminder with a reschedule link.
- Keyword “CHANGE” routes to agent-assisted flow.
Promotions for Opted-In Subscribers
- WhatsApp (Primary)
- Use marketing templates with carousels or product lists.
- Segment by behavior and preferences.
- SMS (Fallback)
- Send concise copy with:
- One clear offer.
- A clean landing page link.
- Always respect opt-out rules.
- Send concise copy with:
13. Decision Checklist
Use this checklist to decide whether SMS, WhatsApp, or a hybrid strategy fits your business:
- Customer Location → Are most of your customers in markets with high WhatsApp adoption?
- Opt-Ins → Do you already have explicit WhatsApp opt-ins for marketing and utility messages?
- Rich UI Value → Would features like lists, buttons, or media significantly improve conversion or reduce support time?
- Blended Cost → What’s the true cost comparison: SMS segments vs. WhatsApp template messages in each market?
- Receipts Needed → Do you require read receipts for performance tracking? (WhatsApp = stronger signals.)
- Guaranteed Reach → Do you need to reach any handset universally? (If yes, keep SMS in the mix.)
- Operational Readiness → Can your team handle template approvals and 24-hour session rules on WhatsApp?
Summary: If your audience is WhatsApp-heavy and you want rich, interactive flows, lead with WhatsApp. Keep SMS for reach, fallback, and compliance coverage.
14. Implementation in 30–60 Days (Suggested Plan)
Here’s a phased rollout strategy to get live quickly while staying compliant:
Week 1–2: Foundation Setup
- Map top markets and adoption rates.
- Review consent records for SMS and WhatsApp.
- Complete WhatsApp Business verification.
- Set up your WhatsApp number(s).
Week 3–4: Content & Capture
- Build WhatsApp templates for:
- Utility (e.g., order updates).
- Authentication (e.g., OTPs).
- Marketing (e.g., product lists).
- Draft SMS copy sets for fallback.
- Add opt-in capture points across:
- Website.
- Mobile app.
- Checkout flows.
- QR code campaigns.
Week 5–6: Pilot & Tune
- Roll out in a pilot market:
- WhatsApp as the primary channel.
- SMS as fallback.
- Track key metrics:
- Delivery rates.
- Read rates (WhatsApp).
- Response times.
- Costs per channel.
- Tune:
- Routing logic (primary vs. fallback).
- Content effectiveness (SMS short copy vs. WhatsApp buttons).
Summary: In 6 weeks, you can have a hybrid WhatsApp + SMS program live, with compliance, consent capture, and performance metrics in place.
SMS vs WhatsApp: Executive Comparison Cheat Sheet
| Dimension | SMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Reach | Universal → works on virtually any handset worldwide. | Massive but regional → strongest in India, Brazil, LATAM, ME, EU; weaker in U.S. |
| Message Formats | Plain text, limited MMS (images/media; support varies). | Rich media: images, video, files, location, catalogs, buttons, lists. |
| Length Limits | 160 GSM-7 chars (70 Unicode); splits into segments if longer. | No practical character limit; structured flows via templates. |
| Interactivity | Links + basic keywords (“STOP”, “HELP”). | Interactive → buttons, quick replies, product pickers, two-way chat. |
| Receipts | Delivery receipts (carrier-dependent); no read receipts. | Strong telemetry: sent, delivered, read (users can disable read). |
| Compliance | Consent required for marketing (TCPA, GDPR, DLT in India). Supports STOP/HELP, DND lists. | Explicit opt-in required; 24h session window; templates for outbound marketing. |
| Pricing Model | Per-message segment; varies by destination, type, surcharges. | Category-based: Marketing, Utility, Authentication. Free replies in 24h window. |
| Deliverability | Dependent on carriers, sender ID quality, regional rules (DLT). | Platform-native → resilient media delivery + template quality rating. |
| Security | Not end-to-end encrypted. Use short OTP expiries, rate limits. | End-to-end encrypted. Templates + policies reduce spam. Stronger for sensitive use. |
| Setup Speed | Usually fast; may require sender ID/template registration in some countries. | Requires business verification, number setup, template approvals, opt-in collection. |
| Best Use Cases | OTPs, alerts, fallback channel, universal transactional reach. | Customer support, guided flows, re-engagement, media-rich experiences. |
Decision Quick-Check
- Need universal reach + simplicity? → SMS
- Need rich flows + engagement + receipts? → WhatsApp
- Need both? → WhatsApp primary, SMS fallback.
Bottom Line:
The best programs don’t choose between SMS and WhatsApp. They orchestrate both:
- SMS for reach + reliability.
- WhatsApp for conversation + conversion.
- Together for resilience, compliance, and cost control.